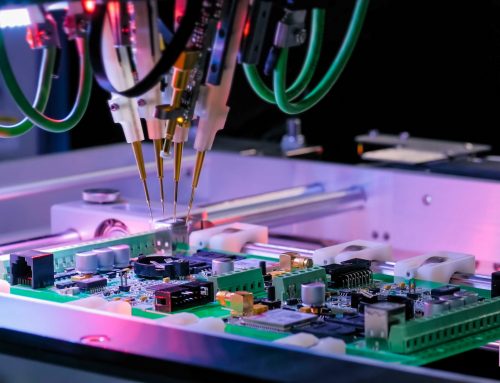
In an industrial context, there are numerous ways to manufacture parts for specific applications.
Some of the most common methods include die casting or machining of components. While die casting involves pouring molten material into a mould, machined parts are manufactured by cutting away material into the desired shape using a programmable robotic arm.
One of the most famous examples of precision machining is the Apple MacBook laptop — its iconic metal body is milled from a single aluminium block! Connectors, electrical crimps and contacts are some other examples of electronic components that are manufactured in this way.
Given the precision machining parts offers, many industries now rely on this method to meet stringent quality standards. But what are some of the other benefits and uses?
Key characteristics
Machined parts refer to practically any component used as a part of a larger piece of equipment, cut to fit exact measurements.
These parts are unique in that they can be made of practically any material. Some of the most common raw materials used in precision machining include stainless steel, brass, aluminium, copper, basic plastics and engineered plastics. Each substance offers different benefits to each application, such as the conductivity of particular metals or the lightweight, biocompatibility of titanium. This versatility means machining of parts can be used across multiple industries to cater to exact specifications.
The process of machining parts also involves programming the dimensions for incredibly precise results and exceptionally tight tolerances. Thanks to this guaranteed accuracy, machining parts allows for quicker assembly, making the process much more cost-effective — perfect for mass production.
OEMs often turn to 3D printing for accurate manufacturing of parts, too. However, precision machining involves the subtraction of material from a raw whole, where 3D printing is an additive process. 3D printing is also used predominantly for plastics and to a lesser extent for metals. In this way, machining is arguably superior as it results in higher quality prototypes with better surface quality.
Versatile applications
Many industries require bespoke parts for equipment, often with exact measurements for intricate and niche applications.
Commercial
In the commercial sector, prototypes and 3D models are often required during the early scoping phases of a product. Precision machining ensures the prototype is an accurate reflection of the end product. Machined parts are also essential for mass production on a commercial scale because they can be manufactured quickly with consistent repeatability.
Medical
In one of our recent blogs about MedTech, we looked at the importance of accuracy in the medical industry, where it truly is a matter of life and death. Machined parts require minute and refined details for specialist medical equipment. Examples of these parts in the healthcare sector include implants, MRI machines, items made from high-temperature plastics and electronics enclosures for monitoring machinery, to name a few.
Aerospace
Fine-tuned, sensitive equipment can also be found in the aerospace industry. Here, any errors could be detrimental. As such, only the most detailed and high-quality parts will suffice. Machined components are used in applications such as turbo engine parts, bushings, air foils and fuel tanks — all of which are put under immense pressure and loads.
Defence
Weaponry and militia benefit greatly from machined parts, incorporated in communications equipment and tank components, for example. Not only are these parts held to an incredibly stringent quality standard, but they also require manufacturing in line with specific requirements and accreditations.
Electronics
As our area of expertise here at EC, we know how important it is that delicate parts for microelectronics are manufactured with the utmost precision. Being so much as a nanometre out of line could make or break the equipment. You can find machined parts in a variety of electronics, such as connectors and electrical crimps. Bespoke connectors and electrical crimps often require tiny micro-components manufactured with miniscule details which only the precision of machining can achieve.
The advantage of outsourcing
Choosing an expert with the right equipment to machine your parts is essential. As the scope for human error is significantly reduced through precision machining, it makes sense to opt for a firm with quality machinery and the knowledge and skill needed to make the most of it.
This means you will be able to trust the parts will be of consistently high quality and reliable — to offer increased levels of safety and functionality.
At EC Electronics, we have built up a strong reputation for producing high-quality electronics-based products, using the latest state-of-the-art equipment. Our team of experts can provide engineering support to any OEM looking to embark on the next “big thing”.
Looking to outsource your next project? Contact one of the friendly team at EC Electronics today!